
Microsurgery for Male Fertility
Home Microsurgery for Male Fertility


Home Microsurgery for Male Fertility
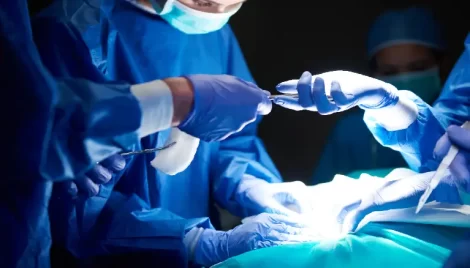
Infertility affects millions of couples worldwide, with male factors accounting for nearly 40-50% of all cases. While lifestyle, hormonal imbalance, and genetic disorders often play a role, structural or anatomical issues are commonly overlooked. Fortunately, advancements in medical science have made it possible to correct many of these problems through microsurgery for male fertility. This highly specialized field combines the precision of microscopic techniques with surgical skill to restore or improve male reproductive function.
Male infertility refers to a man’s inability to cause pregnancy in a fertile female. It is typically diagnosed after one year of regular, unprotected intercourse fails to result in conception. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), male infertility contributes to nearly half of all infertility cases globally.
Varicocele
Obstructive azoospermia
Ejaculatory duct obstruction
Congenital absence of vas deferens
Infections and STDs
Testicular trauma or torsion
Hormonal imbalances
Lifestyle factors (e.g., smoking, alcohol, obesity)
Exposure to toxins or radiation
Genetic disorders (e.g., Klinefelter syndrome)
While lifestyle modifications and medications can improve fertility in some cases, surgery is often necessary when structural blockages or vascular issues are the underlying causes. This is where microsurgical intervention becomes critical.
Microsurgery is typically performed by a urologist or andrologist with advanced training in microsurgical techniques.
Palpable varicocele with abnormal semen analysis
Pain or discomfort due to varicocele
Hormonal imbalance (low testosterone)
This surgery corrects dilated scrotal veins (varicoceles) that impair testicular function. Using a microscope, the surgeon ligates the faulty veins while preserving lymphatic vessels and arteries. The subinguinal approach is most common due to its minimal invasiveness and high success rates.
Improved sperm count and motility
Enhanced testosterone levels
Reduced testicular discomfort
Improved pregnancy outcomes
Men seeking to restore fertility after vasectomy
This involves reconnecting the severed ends of the vas deferens to reestablish sperm flow. A high-powered microscope helps align the inner and outer layers of the vas deferens, which is only 0.3–0.5 mm in diameter.
Patency rates: 80–90%
Pregnancy rates: 40–70%
Epididymal obstruction due to infection, trauma, or congenital issues
This is a more complex surgery than vasovasostomy, where the vas deferens is connected directly to the epididymis. It requires advanced microsurgical expertise due to the fragile nature of the epididymal tubules.
Effective in treating obstructive azoospermia
Restores natural conception potential
Used in cases of obstructive azoospermia, where sperm production is normal but cannot reach the ejaculate.
TESE involves retrieving sperm directly from testicular tissue.
Micro-TESE is a refined version where an operating microscope helps identify areas with active sperm production.
Non-obstructive azoospermia
Genetic disorders
Previous failed ART cycles
Ejaculatory duct obstruction (EDO) causing low semen volume, azoospermia, or pain
Transurethral resection of the ejaculatory duct (TURED) is done using endoscopic and microscopic guidance to relieve the blockage.
High precision with minimal tissue damage
Better preservation of surrounding structures
Reduced risk of complications
Faster recovery
Improved fertility outcomes
Minimally invasive in many cases
Semen analysis (volume, count, motility, morphology)
Scrotal ultrasound (to detect varicocele or structural abnormalities)
Hormonal profile (FSH, LH, testosterone, prolactin)
Genetic testing (Y chromosome microdeletions, CFTR mutations)
Testicular biopsy (in selected cases of azoospermia)
MRI or TRUS (for ejaculatory duct evaluation)
Avoid strenuous activities for at least 1–2 weeks
Use scrotal support for comfort
Abstain from sexual activity for a few weeks
Follow prescribed medications and antibiotics
Semen analysis is repeated 3 months post-surgery, then every 3–6 months
Hormonal levels may also be tracked in varicocelectomy cases
IVF/ICSI planning if natural conception is not achieved within 12 months
| Procedure | Patency Rate | Pregnancy Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Microsurgical Varicocelectomy | 80–90% | 30–60% |
| Vasovasostomy | 80–90% | 40–70% |
| Vasoepididymostomy | 60–70% | 20–40% |
| Micro-TESE (for non-obstructive azoospermia) | 40–60% sperm retrieval | Depends on ART |
The success of the procedure also depends on:
Duration of infertility
Age and fertility status of the female partner
Skill and experience of the surgeon
Presence of underlying testicular damage
Emerging robotic-assisted systems are enhancing precision and reducing surgeon fatigue, particularly in complex reconstructions.
Still under research, these therapies aim to regenerate damaged sperm-producing tissue.
AI tools can improve diagnostics and guide surgical decisions by analyzing sperm patterns and testicular architecture in real-time.
If you’re facing male infertility, consult a qualified urologist or andrologist trained in microsurgical techniques. With the right diagnosis, timely intervention, and expert care, parenthood can become a reality.
Get details in your inbox right now


D 9/90-Opposite Swaminarayan mandir gate no-1, Chitrakoot, Vaishali Nagar, Jaipur, Rajasthan 302021.
Customer Support
+91 82398 88451Drop Us an Email
info@drarjunsinghshekhawat.com
© 2025 Dr. Arjun Singh Shekhawat, All Rights Reserved.